Toolbox Talk: Job-Built Ladder Safety
August 20, 2024 2025-03-30 2:47Toolbox Talk: Job-Built Ladder Safety
Job-Built Ladder Safety
Toolbox Talk: Job-Built Ladder Safety
Introduction
Job-built ladders are essential tools for accessing hard-to-reach areas and handling high-traffic tasks. While they offer flexibility and customization, their safety hinges on proper construction and maintenance. This talk will cover crucial guidelines for building and using job-built ladders safely.
Material Quality
1. Choose Quality Lumber
- Lumber Specifications: Use lumber that is finished on all four sides (s4s) and free of sharp edges or splinters. All nails should be fully driven and flush with the surface. The wood must meet or exceed the quality of #1 Hem-Fir to ensure strength and durability.
- Avoid Compromises: Never cut corners with ladder construction materials. A well-constructed ladder is essential to avoid adding unnecessary hazards to your work environment.
Ladder Design and Dimensions
1. Cleat Requirements
- Single vs. Double-Cleat: Use a single-cleat ladder for fewer than 25 users. For 25 or more users, a double-cleat ladder is required.
- Maximum Length: Job-built ladders should not exceed 24 feet in length, excluding any side rail extension above the landing.
2. Side Rail Construction
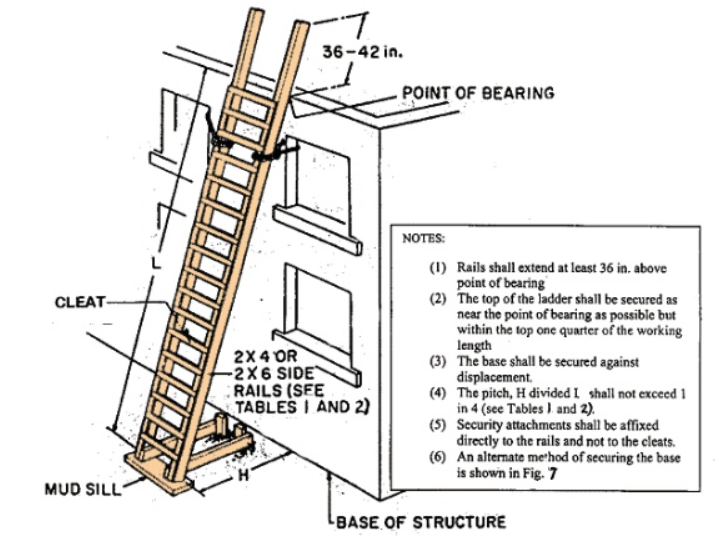
- Extension Above Landing: Side rails must extend 36 to 42 inches above the landing. Construct side rails from either 2×4 or 2×6 lumber. Ladders less than 12 feet high may use 2×4 lumber, while longer ladders must meet ANSI standard A14.4 – 1979 for height and pitch.
- Splicing Rules: Side rails may be spliced once, with the splice located in the upper portion of the rail. The strength of the spliced rail must equal that of an unspliced rail. Ladders with spliced rails should not have a pitch greater than 1-in-8.
3. Cleat Construction and Spacing
- Cleat Material and Installation: Cleats can be made from 1×4 or 2×4 lumber and must run the full width of the ladder. Do not splice cleats. Use three 10d common nails per rail for 1×4 cleats and three 12d nails for 2×4 cleats.
- Spacing: Cleats should be evenly spaced with 12 inches between the top edges of each cleat. There should be no cleats on the portion of the side rails that extend above the landing surface.
- Clearance: For single-cleat ladders, the space between side rails should be 16 to 20 inches. Double-cleat ladders should have 18 to 22 inches between rails, with filler blocks snugly fitted between each cleat. Use 1×2-inch fillers for 1×4 cleats and 2×2-inch fillers for 2×4 cleats.
Inspection and Maintenance
1. Routine Checks
- Daily and Weekly Inspections: Inspect the ladder daily and conduct a more thorough inspection weekly. Examine the ladder’s landings, lashing, connections, and overall condition of the lumber.
- Maintenance: Address any issues immediately and keep cleats clean. Ensure the access point is well-maintained and free of obstructions.
Safety Practices
1. Proper Placement and Security
- Stable Surface: Set the ladder on a level, solid surface to prevent tipping. Avoid placing it in areas where it might be bumped or damaged, such as doorways or driveways, unless the area is clearly marked or barricaded.
- Securing the Ladder: Always secure the ladder at the top and, when possible, secure or stake the bottom to prevent movement.
OSHA: Reducing Falls in Construction: Safe Use of Job-made Wooden Ladders
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3661.pdf
Summary
Safe use of job-built ladders involves:
- Material Quality: Use high-quality, properly finished lumber and avoid shortcuts.
- Design Specifications: Adhere to length, cleat, and side rail guidelines to ensure stability and strength.
- Inspection: Conduct regular inspections and maintain the ladder in good condition.
- Safety Placement: Position the ladder on a stable surface, avoid obstructed areas, and secure it properly.
By following these guidelines, you can help prevent accidents and ensure a safer work environment when using job-built ladders. Remember, proper ladder safety starts with careful construction and consistent maintenance.





