OSHA Training Requirements for Ladder Safety in the Workplace
OSHA Training Requirements for Ladder Safety in the Workplace
Ladders are essential tools in many industries, but they can also pose significant risks if not used properly. Each year, thousands of workers are injured due to ladder-related accidents. According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), falls from ladders are a leading cause of workplace injuries and fatalities. The good news is that most ladder accidents can be prevented through proper safety training, correct ladder selection, and adherence to OSHA regulations. In this blog, we will discuss ladder safety, focusing on OSHA requirements, the importance of safety training, and best practices for ladder use, maintenance, and storage.
The Importance of Ladder Safety Training
The foundation of any effective ladder safety program is safety training. Comprehensive ladder safety training ensures that workers understand the risks associated with ladder use, how to properly operate ladders, and how to select the right ladder for the job. OSHA training and safety courses can make a significant difference in reducing the number of ladder-related accidents in the workplace.
Safety training programs can be tailored to the needs of various industries, and in recent years, online safety training has become a highly effective way to deliver essential information to workers. With the convenience of online safety and health training, employees can learn about ladder safety at their own pace, ensuring that they understand the material thoroughly. Online safety training can cover essential topics such as the correct use of different types of ladders, the proper inspection procedures, and how to spot potential hazards that could lead to an accident.
Additionally, OSHA courses are specifically designed to help employees comply with federal safety regulations. These safety courses typically include practical advice on ladder safety, including OSHA’s requirements for ladder use, inspection, and maintenance. Taking these safety courses ensures that workers are equipped with the knowledge they need to stay safe while using ladders on the job.

Construction Industry Standard for Ladders
In the construction industry, OSHA has specific standards for ladder safety outlined in 29 CFR 1926 Subpart L. These regulations set forth requirements to ensure workers’ safety when using ladders, including specifications for ladder design, maintenance, and use. For example, OSHA mandates that ladders must be inspected regularly, that extension ladders must extend at least 3 feet above a landing, and that the 4-to-1 rule (positioning the ladder base one foot away for every four feet of height) be followed. Additionally, OSHA requires fall protection for workers using ladders over 24 feet in height, and it stipulates guidelines for both portable and fixed ladders to prevent accidents. These standards are crucial to minimizing risks associated with ladder use on construction sites.
OSHA Construction Industry Standard
https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1926/1926.1053
OSHA General Industry Standard for Ladders
In general industry, OSHA’s ladder safety standards are outlined in 29 CFR 1910 Subpart D. These regulations provide detailed guidelines for the safe use, maintenance, and inspection of ladders in workplaces outside of construction. Key requirements include ensuring that ladders are maintained in a safe condition, free from defects like cracks or missing rungs, and that they are used at the correct angle (following the 4-to-1 rule). Additionally, OSHA mandates that portable ladders must be placed on stable, level ground, and that fixed ladders over 24 feet in height must be equipped with fall protection systems such as cages or personal fall arrest systems. These standards are designed to protect workers from falls and injuries while using ladders in various industrial settings.
OSHA Standard for General Industry
https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.23
OSHA Requirements for Ladders
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set clear standards to ensure the safe use of ladders in the workplace. OSHA’s ladder safety standards are designed to reduce the risk of falls and other ladder-related injuries. Let’s look at some key OSHA requirements.
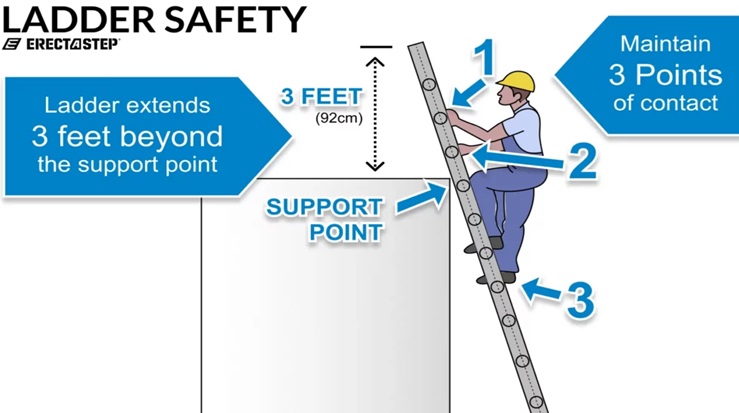
- Ladder Extension: At Least 3 Feet Above the Landing One of the fundamental OSHA guidelines for using extension ladders is that the ladder must extend at least 3 feet above the landing. This extra length allows the user to safely step onto or off the ladder, preventing them from losing balance when climbing or descending.
- The 4-to-1 Rule According to OSHA, for every four feet of ladder height, the base of the ladder should be positioned one foot away from the structure it leans against. This “4-to-1 rule” ensures that the ladder has the correct angle for safe climbing and reduces the risk of the ladder tipping over or sliding.
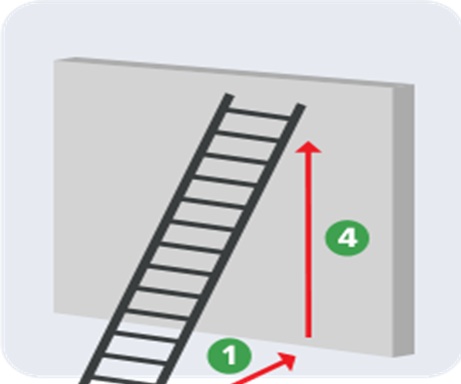
For every 4 feet in height the base of the ladder extends 1 foot away from the structure
Types of Ladders
Safety and health training are very important in construction and other industries. There are several different types of ladders used in workplaces, and OSHA provides specific guidelines for each. Choosing the right ladder for the job is crucial to prevent accidents.
- Portable Ladders Portable ladders are commonly used in a variety of workplaces. These include extension ladders, folding and platform ladders, and articulated ladders. Each type of portable ladder has specific uses and safety considerations.
- Extension Ladders: These ladders are designed to be extended for greater height and are typically used for accessing higher places. It’s essential to ensure that an extension ladder is properly secured at the top and placed at the correct angle (using the 4-to-1 rule) to avoid slipping.
- Folding and Platform Ladders: These ladders are versatile and often used in confined spaces or when mobility is required. OSHA requires that folding ladders be locked in the open position before use to ensure stability.
- Articulated Ladders: These are multi-position ladders that can be used in a variety of configurations. These ladders must be fully extended and locked into place to avoid the risk of collapse.
- Straight or Single Ladders: These are one-section ladders used for lower heights. When using a single ladder, it must be placed at the correct angle and the top should rest securely against a firm, stable surface.
- Job-Made Ladders: These are ladders built on the job site, usually by the employer or contractor. OSHA requires that job-made ladders meet specific design and material requirements to ensure they are safe for use.
OSHA Portable ladders
https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/standardinterpretations/2004-02-26
Reducing Falls in Construction: Safe Use of Extension Ladders
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3660.pdf
Fixed Ladders and OSHA Requirements
There are special requirements for fixed ladders that can be thought through safety and health training. Fixed ladders are permanently attached to a structure, such as a building or scaffolding, and are often used for accessing rooftops, tanks, or other elevated areas. OSHA has specific guidelines for the use and installation of fixed ladders to minimize the risk of falls.
- Fall Protection: OSHA requires that fixed ladders over 24 feet in height be equipped with fall protection systems, such as a cage or personal fall arrest system, to protect workers from falling.
- Rung Spacing: Fixed ladders must have rung spacing that does not exceed 12 inches to ensure safe climbing and descending.
- Clearance: Fixed ladders must provide-sufficient clearance between the rungs and the surrounding structure to allow the user to safely climb.
- Maintenance: Fixed ladders must be maintained in good condition and free from rust, corrosion, or other hazards that could compromise their stability.
Three Points of Contact
Three points of contact should be practiced by employees during safety training. The principle of maintaining three points of contact when using a ladder is crucial for safety and stability. It means having two hands and one foot, or two feet and one hand, in contact with the ladder at-all times while climbing or descending. This reduces the risk of falling by ensuring that the user remains balanced and has a secure grip. By maintaining three points of contact, the ladder user can better respond to any shifts or slips, reducing the likelihood of losing control and preventing accidents or injuries. This simple practice enhances overall stability and helps keep the climber focused on the task at hand.
Ladder Inspection and Maintenance
Demonstrations are key elements of safety training which can teach employees how to perform routine ladder inspections which are critical to maintaining workplace safety. OSHA requires that ladders be inspected before every work shift to ensure they remain in good working condition. Inspections should include checking for:
- Cracks or damage to the ladder’s structure
- Loose or missing rungs
- Rust, corrosion, or other signs of wear
- Worn or slippery feet
- Stability when placed on the ground
Ladders should be maintained according to manufacturer recommendations and replaced when necessary. Regular training on how to inspect and maintain ladders can help ensure that all workers are aware of potential hazards and can take proactive steps to address them.
Ladder Selection
Safety training is significant in any workplace as selecting the right ladder for the job is critical to ensuring safety. OSHA regulations stress that workers should only use ladders that are designed for the tasks they are performing. When choosing a ladder, consider the following:
- Height Requirements: Choose a ladder that allows you to reach the required height without overreaching. Using a ladder that is too short can lead to instability, while using a ladder that is too tall can increase the risk of a fall.
- Weight Capacity: Ladders are rated based on their load capacity, and it’s essential to select a ladder with an appropriate weight limit for the worker and any equipment being used.
- Material: Ladders come in various materials, including wood, aluminum, and fiberglass. When working near electricity, fiberglass ladders are the safest choice as they are non-conductive.
- Condition: Always inspect ladders for damage before use. Never use a ladder that is bent, cracked, or has missing rungs.
Ladder Storage and Transportation
Proper ladder storage and transportation are also important to ensure safety. Ladders should be stored in a dry, secure location to prevent them from being damaged by environmental factors such as rain or direct sunlight. When transporting ladders, ensure they are secured and do not pose a hazard to workers or passersby. OSHA recommends storing ladders horizontally or vertically in a way that prevents them from tipping over or being damaged.
Conclusion
Ladder safety is a critical concern in many workplaces and following OSHA guidelines and participating in ladder safety and health training are essential steps in reducing accidents. OSHA’s ladder safety requirements, including proper ladder extension, correct angle placement, and specific guidelines for portable and fixed ladders, are designed to protect workers and prevent falls. Additionally, online safety training and OSHA courses provide workers with the knowledge they need to use ladders safely and effectively.
By selecting the right ladder for the job, inspecting and maintaining ladders regularly, and following proper storage and transportation procedures, employers can minimize the risk of ladder-related injuries. With the right training and adherence to safety standards, ladder accidents can be greatly reduced, creating a safer work environment for everyone.
Author: Dr. O’Neil G. Blake, Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of OSHAccredited Safety Institute
MS., MBA., MSc., BSc, CSP., ASP., CSHM., CSMP., MRSA.
Date: 12-27-2024










