The Dangers of Permit Required Confined Space
The Dangers of Permit Required Confined Space
In the realm of workplace safety, certain environments pose unique challenges that demand meticulous attention and stringent protocols. Among these, confined spaces stand out as potentially hazardous zones requiring special precautions. In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates guidelines for working in confined spaces through its regulation 1910.146, commonly referred to as Permit Required Confined Space (PRCS) standards. This comprehensive set of regulations aims to mitigate risks and ensure the safety of workers entering confined spaces. Safety and health training must be looked at as the cornerstone for providing employees with the knowledge, skills and awareness to enter permit required confined spaces.
What is A Permit Required Confined Space?
Occupational safety and health training can equip workers with the knowledge and skills to work safely in permit required confined spaces. A Permit Required Confined Space (PRCS) is a designated area within a workplace that meets specific criteria outlined by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), including limited entry and exit points, lack of ventilation, and potential hazards such as toxic gases or low oxygen levels. To enter a PRCS, workers must obtain a permit that outlines safety procedures, including atmospheric monitoring, ventilation, and rescue protocols. These spaces pose inherent risks to workers’ health and safety, necessitating strict adherence to safety guidelines and thorough training to mitigate potential hazards. Failure to comply with PRCS regulations can result in serious injuries or fatalities, making it imperative for employers to prioritize safety measures and ensure proper protocols are followed when working in confined spaces.
OSHA Permit- Required Confined Space 1910.146
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/osha3138.pdf

The Dangers of Permit Required Confined Space
It is very important for companies to develop and implement an effective confined space program to reduce fatalities. According to OSHA, as reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics in July 2020, there were 1,030 worker fatalities in confined space incidents from 2011 to 2018, with 61 of these fatalities occurring specifically in sewers, manholes, and storm drains. Certain types of incidents are closely associated with confined spaces. From 2011 to 2018, trench collapses resulted in the deaths of 168 workers, with 135 of these fatalities occurring in the private construction industry. Falls to a lower level accounted for 156 out of the total 1,030 confined space fatalities during this period, with silo and grain bin interiors (17), sewers, manholes, and storm drains (16), and ditches, channels, trenches, and excavations (15) being the most common coded confined spaces in falls. Inhalation of harmful substances in confined spaces caused 126 fatalities over the 8-year period, with hydrogen sulfide (38 cases), carbon monoxide (23), methane (10), sewer gas (6), and solvents and degreasers (5) being the most prevalent. Additionally, there were 39 cases of oxygen depletion and 21 cases of drowning. Ninety-eight workers lost their lives in incidents involving engulfment in confined spaces, with 66 of these fatalities related to engulfment in cash grain crops or field crops. Fires and explosions accounted for 58 fatalities, predominantly from explosions (46). Caught-in-running-machinery incidents led to 56 deaths, with powered conveyors, particularly screw or auger conveyors (15), being the most common machinery involved in these incidents, totaling 21 cases. These incidences could have been prevented through high quality online safety training.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: Injuries, Illnesses, and Fatalities
https://www.bls.gov/iif/factsheets/fatal-occupational-injuries-confined-spaces-2011-19.htm
The Importance of PRCS 1910.146
The importance of PRCS 1910.146 cannot be overstated, as it serves as a critical framework for safeguarding the lives and well-being of workers who operate in confined spaces. It is important to note that companies can meet OSHA compliance by adhering to the fundamental principles of safety and health training and establishing stringent guidelines and protocols set out in the PRCS 1910.146 standards. Online safety training can help employers and employees identify, assess, and mitigate the unique risks associated with confined space work, including exposure to hazardous atmospheres, limited entry and exit points, and the potential for engulfment or entrapment. Through proactive initiatives such as comprehensive safety and health training, atmospheric monitoring, and rescue procedures, PRCS 1910.146 aims to minimize the likelihood of accidents and fatalities, thereby ensuring that workers perform their duties safely and effectively. Companies that meet OSHA compliance with the PRCS regulations not only protects individual workers but also promotes organizational resilience, productivity, and reputation, underscoring the paramount importance of adhering to these vital safety standards
The Permit System
The Permit System, integral to PRCS 1910.146, is a structured approach designed to ensure the safety of workers entering confined spaces by systematically identifying and mitigating potential hazards. This system mandates that before any entry into a confined space, employers must develop a permit that outlines specific safety measures and procedures to be followed. These safety measures and procedures are vital and can be learnt through occupational safety and health training. This includes conducting thorough atmospheric testing, implementing adequate ventilation, and establishing emergency rescue protocols. The permit serves as a documented authorization, indicating that all necessary precautions have been taken and that workers are aware of the risks involved. By requiring a permit for confined space entry, the Permit System emphasizes proactive risk management, fosters clear communication among workers, and helps prevent accidents and injuries, thus promoting a culture of safety within the workplace.
Northwestern University: Confined Space Entry Permit https://www.northwestern.edu/environmental-health-safety/docs/facility-docs/confined-space-permit.pdf
Atmospheric Testing and Monitoring
Through safety courses employees learn that atmospheric testing and monitoring play a crucial role in ensuring the safety of workers in confined spaces, as mandated by PRCS 1910.146. This process involves the continuous measurement and analysis of the air within a confined space to detect the presence of hazardous gases or other contaminants. Before entry, employers must conduct thorough atmospheric testing to assess the air quality and identify potential risks. This typically includes monitoring for oxygen levels, combustible gases, and toxic substances that could pose a threat to workers’ health and safety. Additionally, monitoring must be ongoing throughout the duration of work in the confined space to detect any changes in atmospheric conditions that may occur due to factors such as equipment operation or chemical reactions. By providing real-time data on air quality, atmospheric testing enables employers to implement appropriate control measures, such as ventilation or respiratory protection, to mitigate risks and ensure a safe working environment for employees.

Employers are responsible for ensuring that atmospheric testing and monitoring procedures comply with PRCS regulations and industry standards. This entails using calibrated and properly maintained testing equipment, as well as providing safety and health training for employees to gain the knowledge and skills to conduct testing effectively. Furthermore, employers must establish clear protocols for interpreting test results and implementing corrective actions in the event of hazardous conditions. By prioritizing atmospheric testing and monitoring, employers can proactively identify and address potential hazards, minimize the risk of accidents and injuries, and uphold their commitment to providing a safe and healthy workplace for all employees working in confined spaces.
OSHA: Procedures for Atmospheric Testing in Confined Spaces
https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/atmospheric_test_confined.pdf
The Four Gas Meter
Online safety training websites that offer safety courses are very popular and are widely available as a training source for employees to gain awareness on the 4-gas meter. The 4-gas meter is a vital tool for testing and monitoring confined spaces, serving as a comprehensive device capable of detecting multiple hazardous gases simultaneously. Typically, these meters measure oxygen levels, combustible gases, and toxic gases such as hydrogen sulfide and carbon monoxide, providing real-time data on atmospheric conditions within the confined space. By utilizing a single device to monitor various gas hazards, the 4-gas meter simplifies the testing process and enhances efficiency while ensuring thorough and accurate assessments of air quality. Its compact and portable design facilitates easy deployment in confined spaces, allowing workers to conduct continuous monitoring throughout their tasks. With its ability to quickly identify potential risks, the 4-gas meter enables employers to implement timely control measures, safeguarding the health and safety of workers and mitigating the potential for accidents or emergencies in confined spaces.

Ventilation of the Space
Ventilation plays a critical role in the safety protocols for permit-required confined spaces due to the potentially hazardous atmospheres they can contain, such as toxic gases or low oxygen levels. Proper ventilation helps to ensure the air within these spaces is safe for workers to enter and work in. By continuously supplying fresh air and removing any contaminants or hazardous gases, ventilation safeguards workers from asphyxiation, poisoning, or other respiratory risks. Additionally, effective ventilation aids in preventing the buildup of combustible gases, reducing the likelihood of explosions or fires within confined spaces. Thus, ventilation not only protects the health and safety of workers but also mitigates the potential for catastrophic incidents, underscoring its indispensable role in confined space operations.
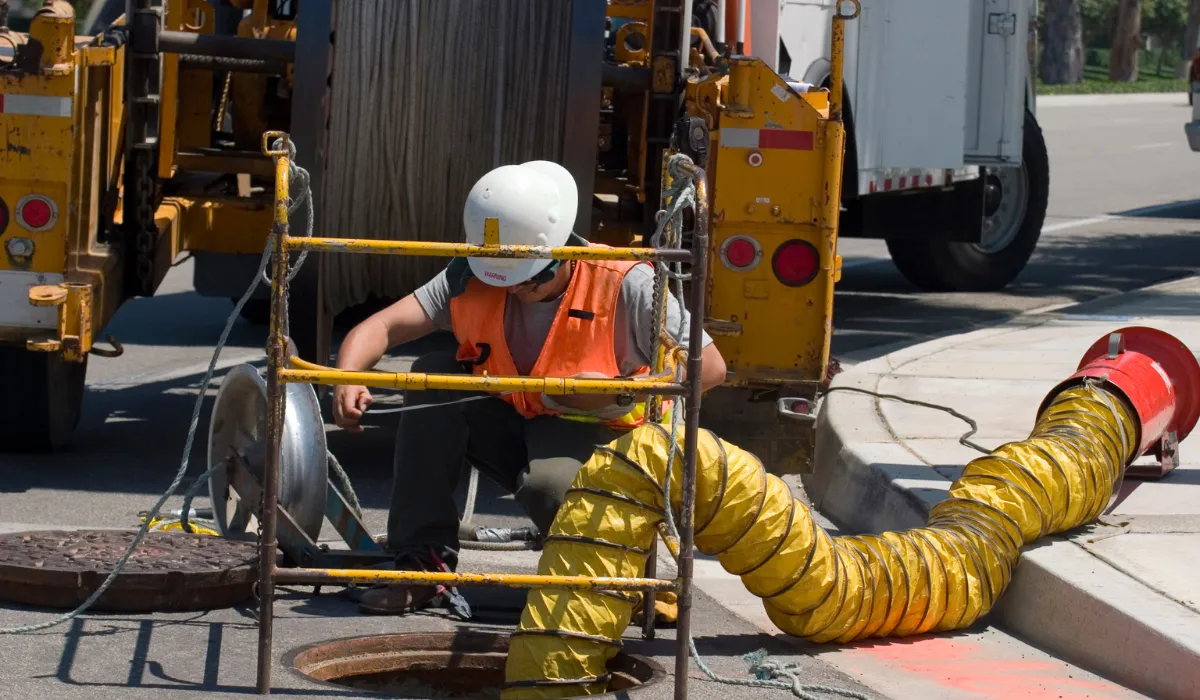

Employee Safety and Health Training Requirements
Providing employee safety and health training requirements under PRCS 1910.146 are paramount for ensuring the safety and competency of workers entering confined spaces. Employers are mandated to provide comprehensive safety training to all personnel involved in confined space entry, equipping them with the knowledge and skills necessary to recognize hazards, utilize safety equipment, and execute emergency procedures effectively. This training typically covers topics such as confined space identification, atmospheric monitoring, proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and rescue protocols. Additionally, workers must be educated on the specific hazards present in the confined space they will be entering and trained to assess risks and respond appropriately. By investing in thorough and ongoing training, employers empower their workforce to work safely in confined spaces, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries and promoting a culture of safety throughout the organization.
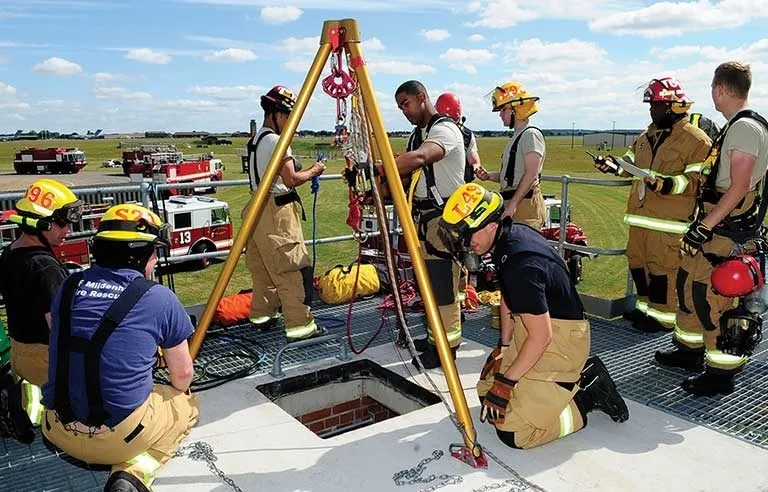

Leadership in Confined Spaces: The Vital Role of Supervisors
Safety and health training are important for workers and supervisors. The supervisor holds a pivotal role in confined space operations, responsible for overseeing and managing all aspects of the work performed within the confined space. As a leader, the supervisor ensures that all safety protocols outlined in PRCS 1910.146 are meticulously followed, including adequate safety training, equipment usage, and adherence to permit procedures. Additionally, the supervisor conducts thorough risk assessments, collaborates with the attendant to monitor atmospheric conditions, and makes critical decisions regarding entry and exit from the confined space. With a keen focus on safety and compliance, the supervisor provides guidance and direction to the team, fosters a culture of accountability, and ultimately, works to mitigate risks and ensure the well-being of all workers involved in confined space activities.
The Entrant’s Role in Confined Spaces
The entrant, as the individual entering the confined space to perform work, plays a crucial role in ensuring the success and safety of confined space operations. Prior to entry, the entrant must undergo comprehensive training on the hazards associated with confined spaces, as well as the specific procedures outlined in PRCS 1910.146. During entry and work within the confined space, the entrant is responsible for following all safety protocols, including wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, continuously monitoring their surroundings for hazards, and promptly communicating any concerns or changes in conditions to the attendant and supervisor. By remaining vigilant and adhering to established safety procedures, the entrant contributes to the overall mitigation of risks and helps ensure a safe and productive work environment within the confined space.
The Crucial Role of Attendants in Confined Spaces
The role of the attendant in confined space entry is integral to ensuring the safety and well-being of workers inside the confined space. Acting as the eyes and ears outside the confined space, the attendant maintains constant communication with workers inside, monitors atmospheric conditions, and oversees the entry and exit process. Additionally, the attendant is responsible for enforcing safety protocols, such as verifying that permits are obtained, ensuring proper ventilation, and coordinating rescue procedures in case of emergencies. By remaining vigilant and attentive, the attendant plays a critical role in identifying and mitigating hazards, facilitating timely responses to changing conditions, and ultimately, safeguarding the lives of workers engaged in confined space operations.
Rescue Training and Procedures
Rescue training and procedures are essential components of confined space safety, ensuring that workers are adequately prepared to respond to emergencies and perform rescues effectively. Employers must provide comprehensive rescue training to personnel involved in confined space entry, covering topics such as rescue equipment usage, communication protocols, and first aid techniques. Additionally, employers must establish clear rescue procedures, including the designation of trained rescue teams and the development of emergency response plans. These procedures outline the steps to be taken in the event of an incident, such as notifying emergency services, assessing the situation, and executing a timely and coordinated rescue operation. By prioritizing rescue training and procedures, employers equip their workforce with the skills and knowledge necessary to respond swiftly and safely in the event of a confined space emergency, ultimately minimizing the risk of injuries or fatalities.
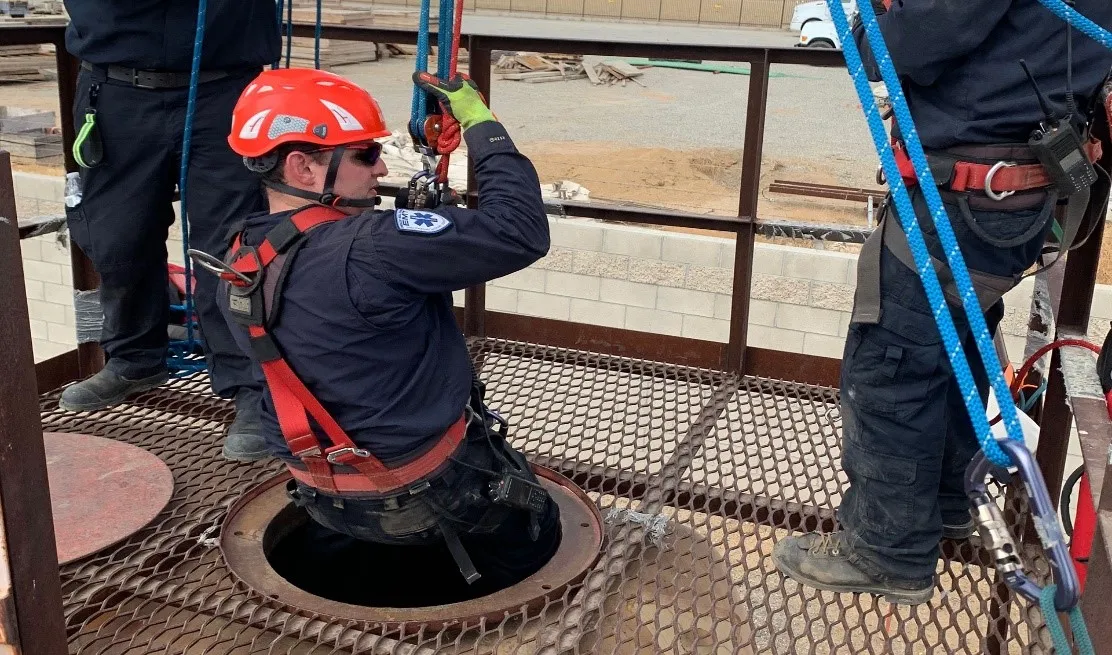

Online Safety Training for General Industry
OSHAccredited Safety Institute offers comprehensive online safety and health training on Confined Space Program. Their curriculum is tailored to meet OSHA compliance requirements of 1910.146 and the specific needs and challenges encountered in permit required confined space. The courses are developed with well-crafted modules, scenarios, videos, and interactive quizzes to support employee learning. To learn more about OSHAccredited Safety Institute and their commitment to promoting safety and well-being in confined spaces, visit their website at www.safetyresultpros.com.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Permit Required Confined Space 1910.146 plays a crucial role in safeguarding the lives and well-being of workers in confined spaces. By adhering to its guidelines and implementing robust safety measures, employers can mitigate risks, prevent accidents, and ensure a safe working environment for all. As we continue to navigate the complexities of workplace safety, it’s imperative that we remain vigilant, proactive, and committed to upholding the highest standards of safety and compliance in confined space operations.
Author: Dr. O’Neil G. Blake, Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of OSHAccredited Safety Institute
MS., MBA., MSc., CSP., ASP., CSHM., CSMP., MRSA.
Date: 04-07-2024